Opsbeacon
Commands
Commands are the core building blocks of your OpsBeacon workflows. Each command represents a specific action that interacts with your configured Connections, enabling seamless automation. Think of commands as individual steps in your workflow, designed to execute precise tasks efficiently.
Types of Commands
OpsBeacon supports the following command types to cater to various use cases:
1. Bash
Execute Bash scripts to automate tasks directly in a Unix-based shell environment. Ideal for running system-level operations. You can execute Bash commands using SSH, Agent or SSM connections.
2. REST
Interact with REST APIs by making HTTP requests. Perfect for integrating with external services or custom APIs. GET, POST, PUT, DELETE and PATCH requests are allowed. You can customize the request body, headers, and query parameters. REST commands can only be used with REST connections.
3. SQL
Perform SQL queries on your databases, enabling seamless data retrieval, updates, or modifications. Keep in mind that SQL commands are only compatible with SQL connections.
4. AWS
Access and manage AWS services directly using predefined actions tailored for cloud automation. These predefined actions in OpsBeacon are given below:
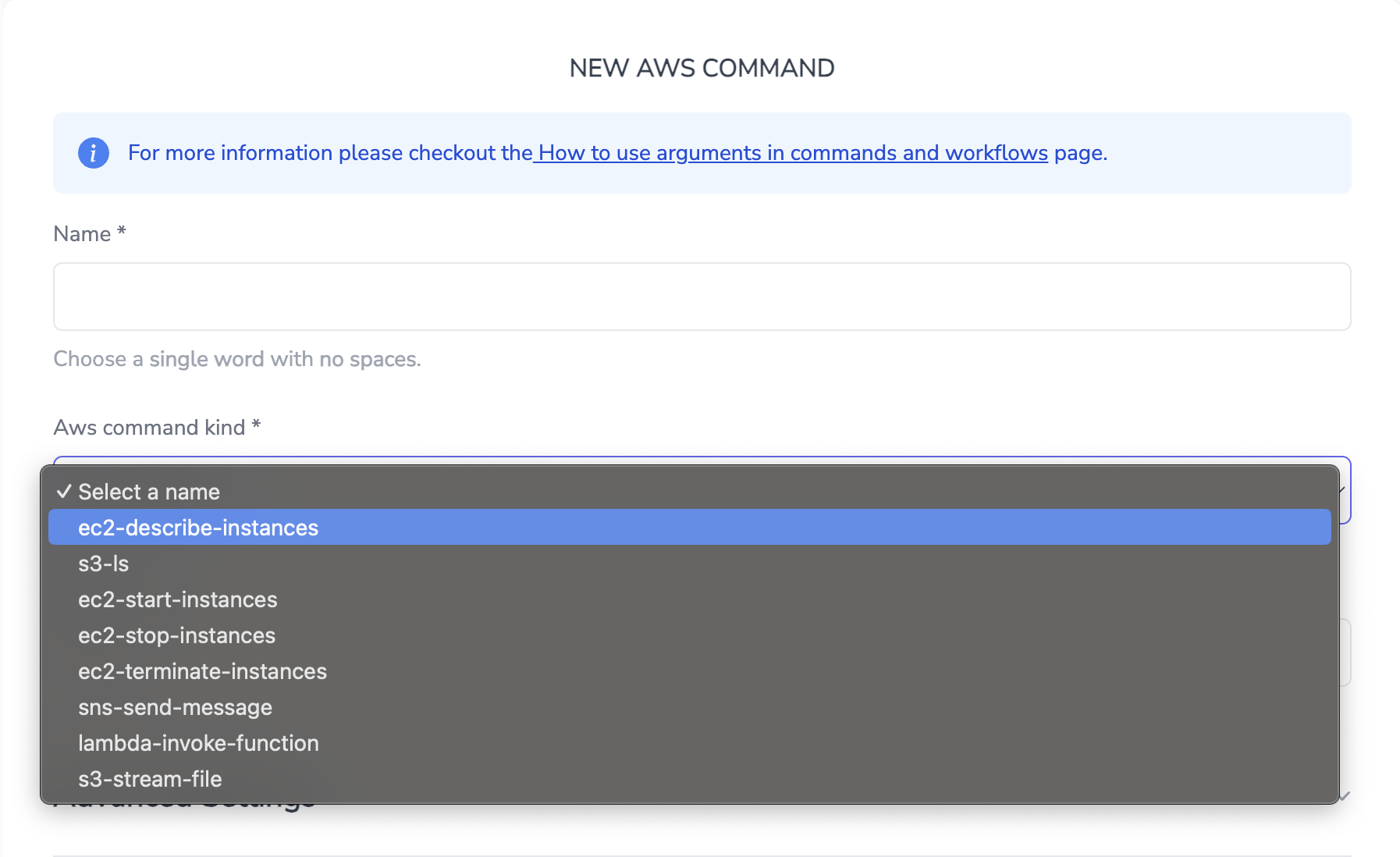
Each action comes with built-in arguments available in the arguments section. If an action has required arguments, they will automatically appear as pre-selected in the arguments section upon selecting the command.
For example, the ec2-stop-instances command requires the instance-ids argument. Both required and optional arguments are displayed as shown below:
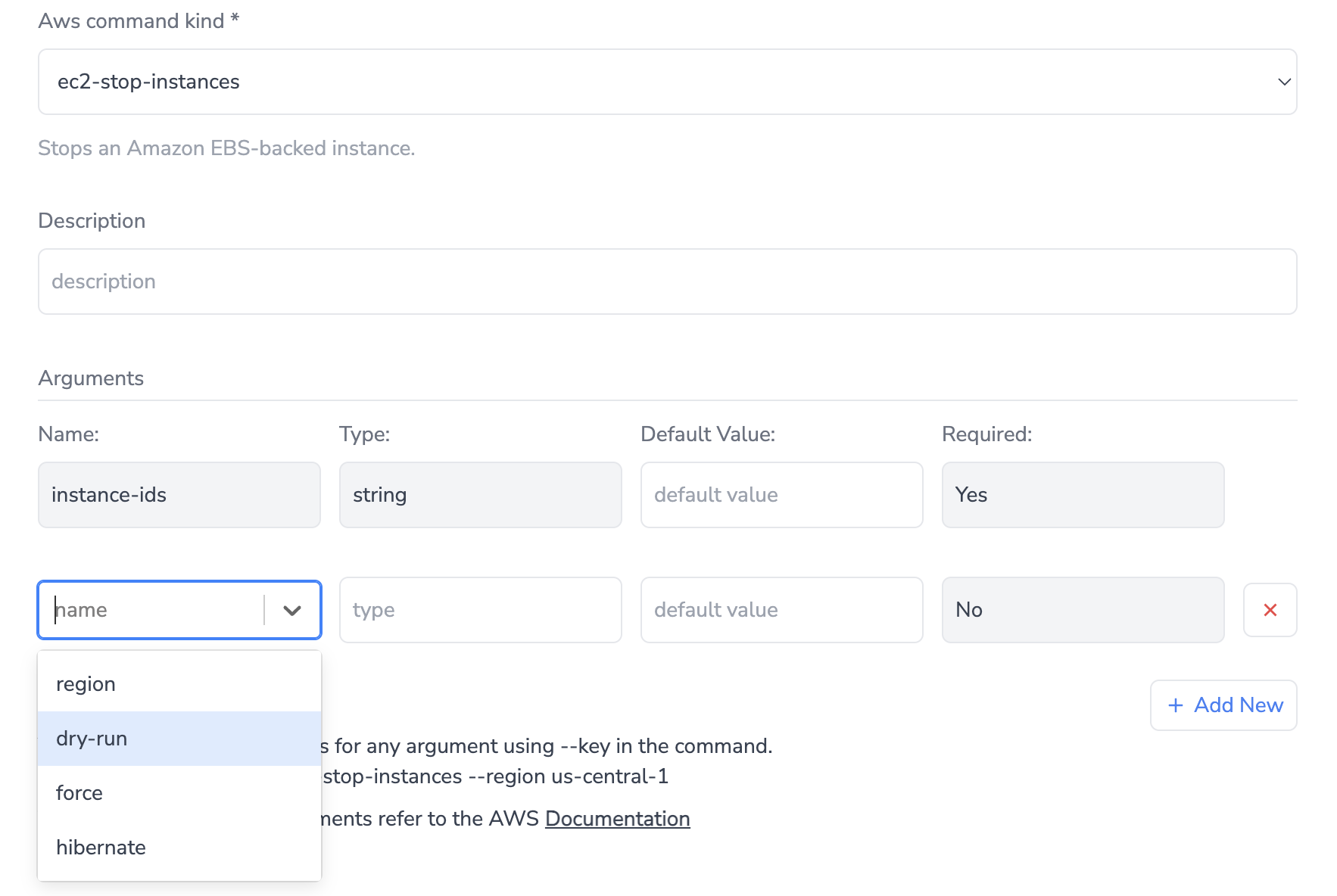
As the name implies, AWS commands are exclusively compatible with AWS connections.
5. Script
Run custom scripts written in a supported language on the corresponding working machine connected via AGENT or SSM connection, providing flexibility for complex or unique tasks. The language used must be supported on the machine where the script is executed.
6. JIRA
Automate JIRA operations, such as creating issues, retrieving ticket details, adding comments to tickets, and changing ticket status. As with AWS commands, required arguments for each action are provided, with the rest being optional. JIRA commands can only be used with JIRA connections.
